

The resultant output is a column vector having an integration result for each row. Trapz is executed on each row of the input numeric ‘Y’ as the value for ‘dim’ is set to 2. The rows in input numeric data ‘Y’ is obtained from velocity data taken at 3 different trials. The point spacing is obtained by matrix ‘X’ which indicates that the trapezoids are formed non-uniformly.
#Matlab integration code
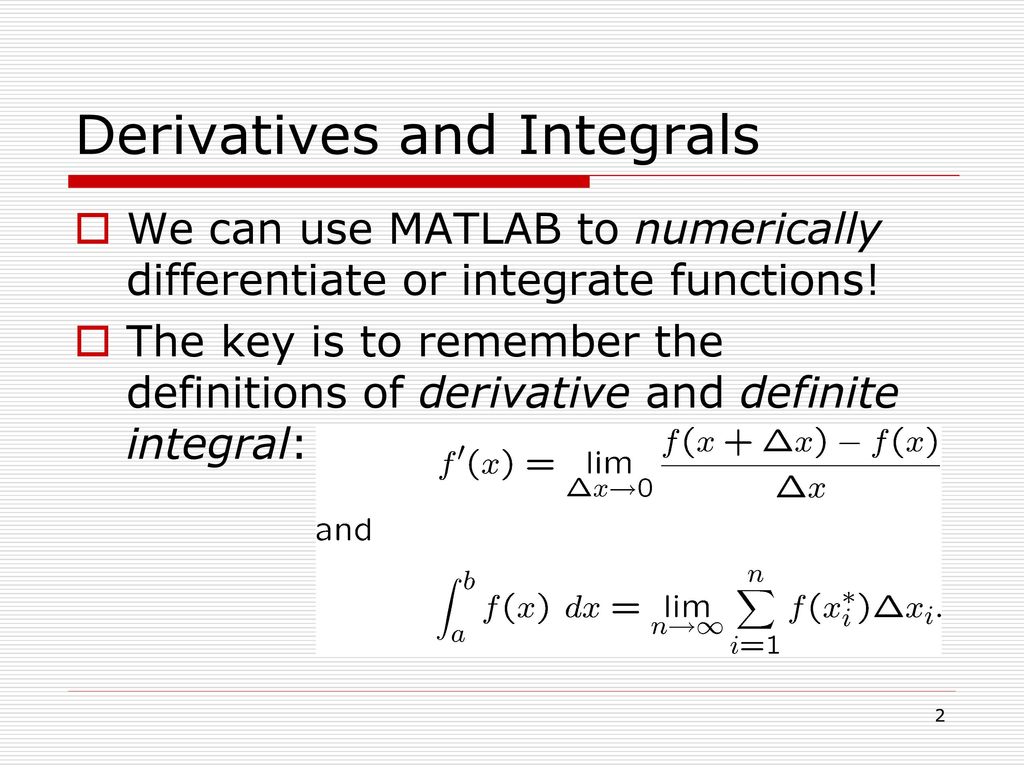
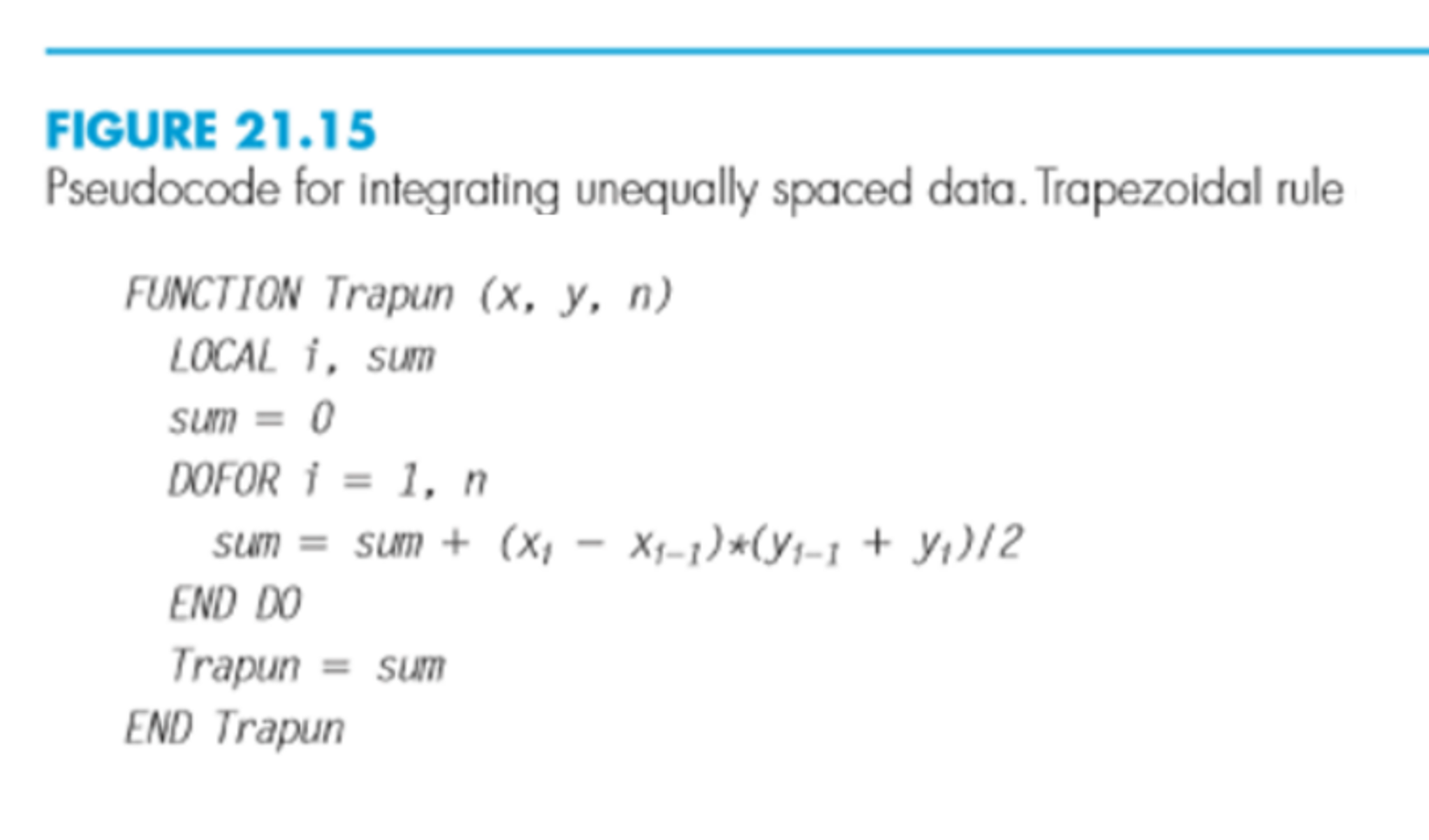
The below code is written to call the trapz function on the input numeric data ‘Y’ with non-uniform point spacing values defined by ‘X’ with the value of ‘dim’ as ‘2’. This operation can be executed by applying the syntax Q = trapz(Y, X, dim) in the trapz function implementation in the MATLAB code. The below code is written to call trapz function on input numeric data ‘Y’ having point spacing value of pi/10.Įxample #3 – Numerical integration with non-uniform spacing This operation can be executed by applying the syntax Q = trapz(Y, X) in the trapz function implementation in the MATLAB code. The below code snippet is written to execute trapz operation on input numeric ‘Y’ as f(x)= 10*2^x.Įxample #2 – Numerical integration with Non-Unit spacing This operation can be executed by applying the syntax Q = trapz(Y) in the trapz function implementation in the MATLAB code. Here are the following examples mention below: Example #1 – Numerical integration with Unit spacing

It operates on elements with columns of ‘Y’, returning a row vector as output. 2 different dimensions in which trapz works are as follows:.Decides the direction along which the integration operation will be performed.The data type supported by ‘X’ are single/ double.X as scalaràIt satisfies the condition as X as vector à The length of the coordinate vector must be equal to the size of the first non-unit sized dimension of the numerical input ‘Y’.Ģ. Value of X of different nature needs to follow come conditions as mentioned below:ġ.The specified point spacing value over which the number of trapezoids to be formed is decided.Y as multi-dimensional arrayà The operation takes place on the first non-unit sized dimension of ‘Y’ and results in the size of value 1 for that dimension while the size of the other dimensions remains unchanged. Y as matrixàThe output is the result of integration operation executed on each column, presented as a row vector of values of the integration operations.ģ.
Y as vector àThe output is an approximated integral result for ‘Y’Ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
